Prof. Dr. Nadine Töpfer
Research focus
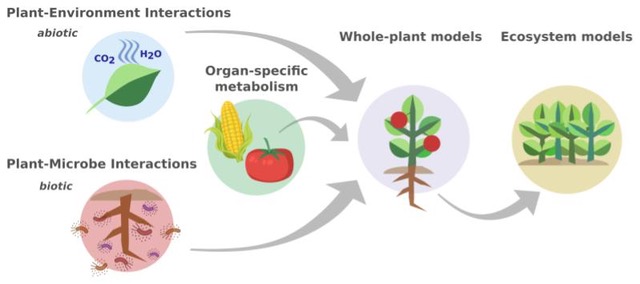
Our research aims to gain a better understanding of the behaviour of plant metabolic systems and their interactions. The group uses computational approaches that are centered around the analysis of large-scale metabolic networks and works closely with experimental labs. Key topics include developing flux-balance methods to study plant metabolism at the cell type-, tissue- and whole-plant level as well as plant-environment interactions. We have also started to develop multi-scale models to better account for genetic, physical, and environmental influences on plant metabolism. On the technical side, we are developing open-source software packages for coherent and reproducible metabolic network curation. The gained knowledge will guide metabolic engineering strategies for improved crop plant productivity and quality.
Most important publications
- Camborda S, Weder JN, Töpfer N (2022) CobraMod: a pathway-centric curation tool for constraint-based metabolic models. Bioinformatics 38(9):2654-2656. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac119.
- Töpfer N (2021) Environment-coupled models of leaf metabolism. Biochem Soc Trans 49(1):119-129. doi: 10.1042/BST20200059.
- Töpfer N, Braam T, Shameer S, Ratcliffe RG, Sweetlove LJ (2020) Alternative Crassulacean Acid Metabolism Modes Provide Environment-Specific Water-Saving Benefits in a Leaf Metabolic Model. Plant Cell 32(12):3689-3705. doi: 10.1105/tpc.20.00132.
- Töpfer N, Fuchs LM, Aharoni A (2017) The PhytoClust tool for metabolic gene clusters discovery in plant genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 45(12):7049-7063. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx404.
- Szymanski J, Levin Y, Savidor A, Breitel D, Chappell-Maor L, Heinig U, Töpfer N, Aharoni A (2017) Label-free deep shotgun proteomics reveals protein dynamics during tomato fruit tissues development. Plant J 90(2):396-417. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13490.
- Sajitz-Hermstein M, Töpfer N, Kleessen S, Fernie AR, Nikoloski Z (2016) iReMet-flux: constraint-based approach for integrating relative metabolite levels into a stoichiometric metabolic models. Bioinformatics 32(17):i755-i762. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw465.
- Töpfer N, Scossa F, Fernie A, Nikoloski Z (2014) Variability of metabolite levels is linked to differential metabolic pathways in Arabidopsis's responses to abiotic stresses. PLoS Comput Biol 10(6):e1003656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003656.
- Recht L, Töpfer N, Batushansky A, Sikron N, Gibon Y, Fait A, Nikoloski Z, Boussiba S, Zarka A (2014) Metabolite profiling and integrative modeling reveal metabolic constraints for carbon partitioning under nitrogen starvation in the green algae Haematococcus pluvialis. J Biol Chem 289(44):30387-30403. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.555144.
- Töpfer N, Caldana C, Grimbs S, Willmitzer L, Fernie AR, Nikoloski Z (2013) Integration of genome-scale modeling and transcript profiling reveals metabolic pathways underlying light and temperature acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25(4):1197-1211. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.108852.
- Töpfer N, Jozefczuk S, Nikoloski Z (2012) Integration of time-resolved transcriptomics data with flux-based methods reveals stress-induced metabolic adaptation in Escherichia coli. BMC Syst Biol 6:148. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-148.
ORCID: 0000-0002-3027-5799